Cells & Tissues of Organisms
Knowledge-based Questions & Answers:
Ques-1. What is cell?
Ans: Cell is the structural and functional unit of an organism.
Ques-2. What is protoplasm?
Ans: Protoplasm is the translucent, semi-fluid, viscous substance inside a living cell.
Ques-3. What is cytoplasm?
Ans: The semifluid, jelly-like substance of a cell that is external to the nuclear membrane and internal to the cellular membrane is called the cytoplasm.
Ques-4. What is plasmalemma?
Ans: The double-layered membrane around the protoplasm of a cell is called plasmalemma.
Ques-5. What is plastid?
Ans: Plastid is an important organelle in a plant cell that contains different colourful pigments.
Ques-6. What is chloroplast?
Ans: Green plastids are called chloroplasts.
Ques-7. What is leucoplast?
Ans: The plastids which don’t contain any colourful pigments are called leucoplasts.
Ques – 8. What is necleoplasm?
Ans: The jelly-like fluid enveloped by the nuclear membrane is called the nucleoplasm.
Ques -9. What is lysosome?
Ans: The cytoplasmic organelle which acts as the reservoir of hydrolytic enzymes is known as lysosome.
Ques -10. What is myosin?
Ans: Myosin is a protein that is used to make fibers for the cytoskeleton.
Ques-11. What is sclerenchyma?
Ans: Tissues composed of cells which are without protoplasm and with the thickening of walls with lignin for providing mechanical support is called sclerenchyma.
Ques-12. What is bast fiber?
Ans: The phloem fibers which are composed of sclerenchyma cells are called bast fibers.
Ques-13. What is metaxylem?
Ans: The matured state of primary xylem is called metaxylem.
Ques-14. What is muscular tissue?
Ans: Growing from the mesoderm of the embryo, the particular type of tissue capable of contracting and expanding is called muscular tissue.
Ques-15. What is connective tissue?
Ans: The tissue in which there are more matrix compared to the number of cells is called connective tissue.
Ques-16. What is glandular tissue?
Ans: The tissue from which necessary fluids are secreted is called glandular tissue.
Ques-17. What is blood?
Ans: Blood is a type of alkaline, slightly saline, red liquid connective tissue.
Ques-18. What is involuntary muscle?
Ans: The muscle whose contraction and expansion doesn’t depend on the will of the animal is called involuntary muscle.
Ques-19. What is an intercalated disk?
Ans: The disk-shaped structures which are seen in the cardiac muscle are called intercalated disks.
Ques-20. What is nervous tissue?
Ans: The particular type of tissue that forms the nervous system is called nervous tissue.
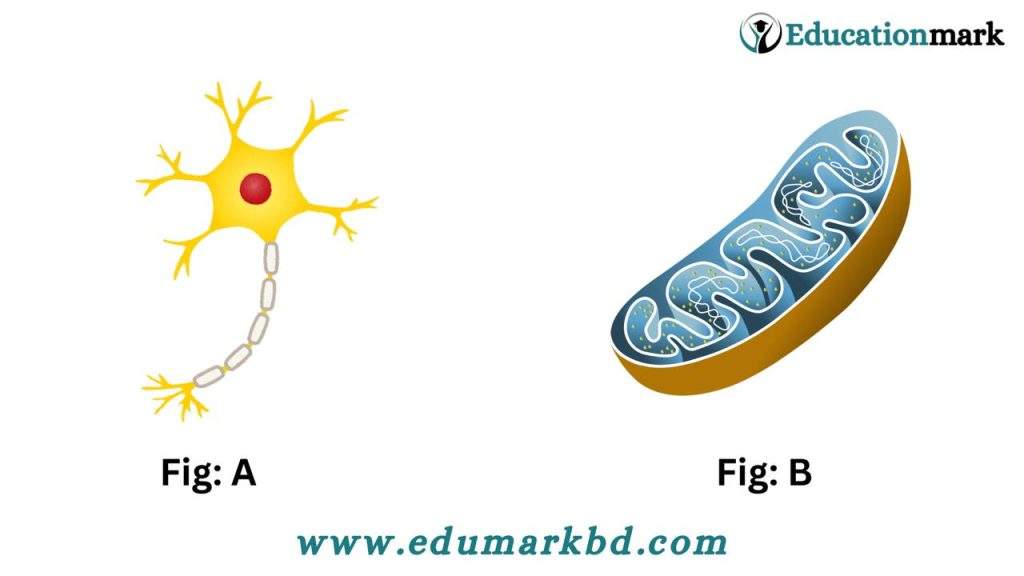
Ques-21. What is dendron?
Ans: The branched fibers arising from the cell body of the neuron are called dendron.
Ques-22. What is neuron?
Ans: The structural and functional unit of the nervous system is called neuron.
Ques-23. What is organ?
Ans: A part of the animal body formed by the combination of one or more than one type of tissues performing a particular function is called an organ.
Ques-24. What is axolemma?
Ans: The covering of the axon is called axolemma.
Ques-25. What is system?
Ans: When several organs function together to perform a similar type of physiological activity in body, then the organs together are called system.
Ques-26. What is electron microscope?
Ans: The microscope in which electron waves are used to magnify images is called electron microscope.
Ques-27. What is body tube?
Ans: It is the tubular part at the upper side of the microscope. One end of it holds the eye piece. The objective lenses are attached at the other end.
Comprehension-based Questions & Answers:
Ques-1. What do you mean by eukaryotic cell?
Ans: The cells in which the nucleus is well structured, meaning that the nuclear materials are well organized and surrounded by a nuclear membrane are called eukarvotic cells. There are two types of eukaryotic cells-somatic cell and gametic cell. In these cells, there are all types of organelles including ribosome. Most of the living cell is eukaryotic cell.
Ques-2. Why are plastids called colour forming organs?
Ans: The colored organelles present within the cytoplasm of plant cells are known as plastids. They are responsible for the formation of color of any plant part like leaves, flower and fruits. In absence of light plastids become colorless. The colorless plastids are known as leucoplasts generally present in the cell of roof and contex where light is not available. In presence of light, colorless plastids may develop color. So the plastids are known as the color forming organelles.
Ques-3. How does skeletal tissue protect the brain?
Ans: Skeletal tissue constitutes the structural framework of animal body, holds the muscles and protects the internal organs from injury. Brain is the most sensitive and important part of the body of vertebrate animals. So, its protection demands highest importance. There is a cover made up of hard bones around the brain known as skull. In the vieinity of the skull brain remain situated and its safety is maintained and protected from external injury.
Ques-4. When chromatin fibres look like as chromosome?
Ans: Chromatin fibers become coiled during cell division and become more condensed, and then they are called chromosomes. Chromosomes carry the units of heredity and pass from generation to generation.
Ques-5. Explain the reason why water-hyacinth floats in water.
Ans: Water hyacinth has a special type of parenchyma tissue called aerenchyma that helps it to float in water. Aerenchyma is a special type of parenchyma tissue that has air filled spaces. They are usually big in size and the air filled spaces work as air bags. They are mostly found in aquatic plants such as, water hyacinths, which helps them to float in water.
Ques-6. What is meant by endocrine gland?
Ans: The glands which are ductless and the secretion from the glands are transported through blood or lymph and act at a distant organ are called endocrine glands. For example-Pituitary gland, thyroid gland, etc.
Ques-7. Why nucleus is called the control center of cell?
Ans: Nucleus is known as the control center of the cell as it performs the following functions: The nucleus contains the hereditary material of the cell, the DNA. It sends signals to the cells to grow, mature, divide and die. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope that separates the DNA from the rest of the cell. The nucleus protects the DNA and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene expression the nucleus is, therefore, the control room of the cell.