Chapter 3: Force
Knowledge-based Questions:
1. What is called force?
Answer: The external cause which changes or tends to change the state of an object is called force.
2. What is inertia?
Answer: The notion of an object in rest to remain at rest or an object in motion to remain in uniform velocity is called inertia.
3. Write down Newton’s first law of motion.
Answer: A stationary object will remain stationary and an object in uniform motion will continue its uniform motion unless a force is applied to it.
4. Write down the Newton’s second laws of motion.
Answer: The rate of change of momentum of a body is proportional to the applied force acting on it and the change of momentum also takes place in the direction in which the force acts.
5. Write down Newton’s third law of motion.
Answer: When an object applies a force on another object, then that object also applies a force of equal magnitude on the first object but in the opposite direction.
6. What is fundamental force?
Answer: Fundamental forces are the four primary forces in nature and all other types of forces can be derived from them.
7. What is gravitational force?
Answer: The force due to which all objects in the universe attract one another is called gravitational force.
8. What is momentum?
Answer: Momentum is the product of mass and velocity of an object.
9. Write down the conservation law of momentum.
Ans: The law of conservation of momentum is:
“If no force is applied from outside in a collision between two objects, the momentum before collision and after collision will be the same.”
10. What is rolling friction?
Answer: When an object moves by rolling or revolving on a surface then the friction that develops is called rolling friction.
11. What is a balanced force?
Answer: If two forces applied to an object are equal and opposite in direction, then these forces are called balanced force.
12. What is static friction?
Answer: The frictional force that develops when two objects are at rest relative to each other is called static friction.
Comprehension-based Questions:
1. Why is the frictional force generated?
Answer: Friction is the consequence of the surface irregularities of any two surfaces. Though the surface of an object seems to be smooth apparently, there are high and low grooves on it in fact. When an object moves on another object, the grooves of both the surfaces catch onto one another and this is why frictional force is produced.
2. Mass quantifies inertia- Explain.
Answer: The characteristic that a stationary body wants to be stationary or a body in motion wants to keep its motion unless a force is applied, is called inertia. Mass is the quantity of matter in a physical body. It is also a measure of the body’s inertia, the resistance to acceleration when a net force is applied. The greater the mass of the body, the greater is its resistance to change its current state of motion or rest. Thus it can be said that, mass quantifies inertia.
3. Why is it easier to walk on hard ground?
Answer: It is easier to walk on hard ground because when we walk on the ground, our body weight sends a force downward due to gravity. According to the 3rd law of Newton, we know that, every action has an equal and opposite reaction. Therefore, as our body pushes the ground, the ground also push us upward with equal force. But if the ground is not solid enough, the upward force is less than the downward force due to weight, which makes it difficult to walk.
Hence, it is easier to walk on a solid ground.
4. Why is it difficult to walk on the sand? Explain it.
Answer: We can explain the mechanism of walking by Newton’s third law, which is, when an object applies a force on another object, then object also applies a force of equal magnitude on the first object but in the opposite direction. When we walk, we exert a force on the ground. According to Newton’s 3rd law, the ground also applies an equal and opposite force on our body. This equal and opposite force creates acceleration, thus we can walk.
But it is difficult to walk on sand rather than hard surface because it is not possible to apply force onto sand. As pressure is applied onto sand, it is displaced. Therefore, the reaction force is less and we face trouble while walking on sand.
5. Why run forward in case of jump from a moving riksha? Explain.
Answer: We run forward when we jump off from a moving rickshaw due to the inertia of motion.
When a rickshaw is on a motion, we are moving with the rickshaw. When we jump off from a moving rickshaw, our body wants to keep going forward due to the inertia of motion. That is the reason we start running forward when we jump off from a moving rickshaw.
6. Why a gun recoils when a bullet comes out from the gun?
Answer: According to Newton’s third law of motion, every action has an equal and opposite reaction. When a gun fires a bullet, the gun puts a force on the bullet that propels it forward. The bullet likewise exerts an equal and opposing force on the gun in the backward direction.
Since the mass of gun is large than the mass of a bullet, so the gun recoil with a velocity much lesser than the velocity with which the bullet moves forward.
7. Mass of object is constant but weight is not constant – explain.
Answer: Mass of an object is actually the amount of matter it contains and it would remain the same unless there is change in the amount of matter whereas weight of an object is the force on it due to gravity. Consider an object with mass 1kg whose weight would be 9.81N approx. on earth. It would be less in Mars due to variation in gravity. Weight of an object varies from place to place due to variation in gravity at different places. There are factors due to which acceleration due to gravity may vary. Like altitude, latitudes and even the spinning of our planet may vary acceleration due to gravity at different places on earth. Sometimes even geological factors account to change in value of acceleration due to gravity.
Creative Questions:
Creative Question 1:
A body of mass 10 kg is at rest. A force of 10 N acts on it for 5 sec. Then the body moves with uniform velocity for 5 sec. Again 5 N force acts on it for 10 sec.
a. Define rolling friction.
b. Mass quantifies inertia- Explain.
c. Calculate the distance covered by the body in first 10 sec.
d. Analyze the motion of the object by drawing velocity vs time graph according to the information of the stem.
[Dhaka Board 22]
Creative Question 2:
A and B are to toy marble stone. At one stage of the game two marbles happen collision face to face and after the collision they continue to move at the uniform velocity.
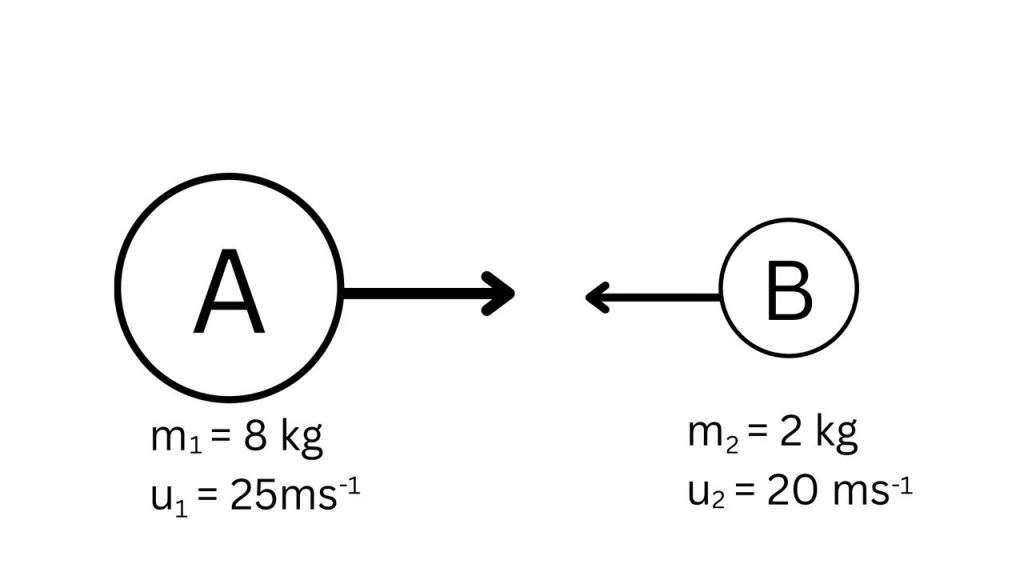
a. What is called velocity?
b. Why is it easier to walk on hard ground?
c. Determine the velocity and direction of the combine stones after collision.
d. Analyze mathematically whether the incident of the stem obeys the laws of conservation of momentum and kinetic energy.
[Mymensingh board]
Creative Question 3:
There is a collision between two bodies which is shown in figure. After the collision the combined body moves towards P.
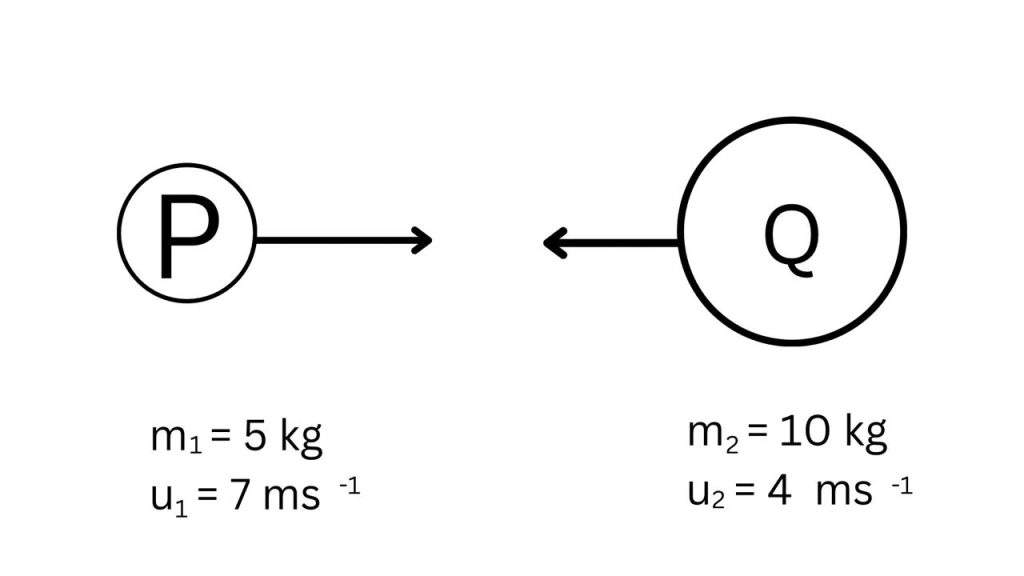
a. What is static friction?
b. Why a gun recoils when a bullet comes out from the gun?
c. Find the impulse of force of the first body after the collision.
d. Is the collision is elastic or not? Explain with mathematical analysis.
